Blog

Income Tax Penalty Chart: Avoid Steep Fines with ClearBiz
Income tax penalty is a word many people dread. The Indian Income Tax Department has the power to impose penalties for various non-compliance and deviations from the provisions of the act. This includes late filing of Income Tax Returns (ITRs), penalties for incorrect reporting of income, wilful non-compliance, and many more provisions. It is worth noting that many of these offences under the Income Tax Act are criminal offences. This means contravention can result in jail terms for the responsible persons
There is a Latin saying, ignorantia juris non excusat which translates as “Ignorance of Law is not an excuse” Understanding and adhering to the law of the land is the responsibility of every citizen. However, for many people understanding the complex provisions of law and preparing documents according to it might be difficult. However, contravention is not a solution. The best way out is to engage a trusted professional who will help you through the process
How is the Income Tax Penalty Calculated ?
The income tax penalty is calculated based on different parameters, Here are some of the most common grounds for charging late fees or penalties
- Late filing of ITR: If the return of Income is filed beyond the due date (31st July for Non-Corporate Business and 30th September for Corporate Assesees.A penalty of Rs. 5,000 is levied for individuals with a total income exceeding Rs. 5 lakhs. For those with income below Rs. 5 lakhs, the penalty is Rs. 1,000.
- Delayed payment of advance tax or self-assessment tax: Advance tax has to be remitted by all taxpayers in 4 installments and the entire liability must be discharged before the 31st of March every financial year interest is charged at the rate of 1% per month from the due date of payment to the actual date of payment in case there is a shortfall or non-payment
- Incorrect or false information: These are some serious non-compliance provisions. If the taxpayer wilfully conceals his income or provides false information in ITR.Penalties can range from 50% to 200% of the tax evaded.
- Non-compliance with TDS/TCS provisions: Penalties can be imposed on the deductor/collector if TDS is not remitted to the government within the 7th of the succeeding month. An interest of 1% per month is charged. Also for delay in filing of TDS Returns, per day late fee of RS 100 is payable subject to a maximum of tax payment
Penalty Chart Under Income Tax Act, 1961
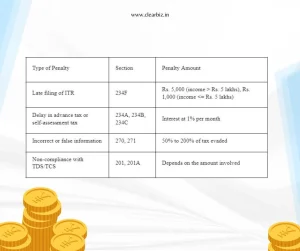
| Type of Penalty | Section | Penalty Amount |
| Late filing of ITR | 234F | Rs. 5,000 (income > Rs. 5 lakhs), Rs. 1,000 (income <= Rs. 5 lakhs) |
| Delay in advance tax or self-assessment tax | 234A, 234B, 234C | Interest at 1% per month |
| Incorrect or false information | 270, 271 | 50% to 200% of tax evaded |
| Non-compliance with TDS/TCS | 201, 201A | Depends on the amount involved |
Note: This is a simplified chart. Actual penalties may vary based on specific circumstances.
What is the Fine Slab for Late Income Tax?
The fine slab for late income tax depends on the income level and the delay period. As mentioned earlier, individuals with an income exceeding Rs. 5 lakhs face a higher penalty compared to those with lower incomes. Additionally, late payment interest is payable at 1% per month for such delay
Can the Income Tax Penalty Be Reduced?
In certain cases, taxpayers can request a reduction in the income tax penalty. This usually requires providing valid reasons for the delay or error. However, the success of such requests depends on the specific circumstances and the discretion of the tax officer.
How Can Avoid Penalty Tax?
To avoid income tax penalties, follow these tips:
- File ITR on time: Adhering to the due dates is important. July 31st for Individuals (Non-Tax Audit ) and 30th September for Audit cases
- Pay advance tax and self-assessment tax on time: Avoid late payment penalties and interest by strictly following the advance tax installments
- Maintain accurate records: Proper documentation helps prevent errors while filing ITR. This in turn ensures there is no mismatch with data available with the Income Tax Authorities
- Seek professional help: Consult a tax expert for guidance, to minimize the possibility of errors and ensure you stay compliant
The Benefits of Filing ITR on Time
Filing your Income Tax Return on time offers several advantages:
- Avoid penalties: As discussed, late filing attracts penalties and interest
- Claim refunds: If you have paid excess in taxes, you can claim a refund by filing the ITR. Now refunds are processed even within a week and disbursed to the tax payer
- Loan approvals: Many financial institutions require ITR for loan processing. ITR are taken as a record for income proof. Usually bankers request for previous three years of ITR as income proof of the applicant
- Visa applications: Some countries require ITR for visa purposes.
Conclusion
Developing an overall understanding of the existing tax laws is a must if you earn income in India. This is not just if you are doing any business here. Even in case you are a salaried person, knowing the basic provisions of Income Tax is extremely important
FAQs On Income Tax Penalty
- What is the maximum penalty for not filing ITR?
The Maximum penalty for non filing of ITR is Rs 5000 , however if your income is below Rs 500,000 late fee u/s 234F will only be RS 1000
- Can we file ITR for last 3 years?
Well now there is a provision to file ITR-U (Updated Return). This can be done for previous 2 years . However this cannot be used for claiming any refund
- What is the penalty for not filing TDS report?
The penalty is Rs 100 per day, limited to the amount of tax remitted
- How to pay late filing penalty?
Income Tax payment can be made by using the E Pay Tax Facility on the ITD Portal
- What is the normal penalty in income tax?
The Maximum penalty for non filing of ITR is Rs 5000 , however if your income is below Rs 500,000 late fee u/s 234F will only be RS 1000, Likewise for each case of contravention from act penalty provision varies under the act
- What is the maximum exemption for ITR?
All individual whose income falls below basic exemption limit (Rs 250000) are not required to file ITR
- What are the steps to Epay Tax
Step 1: Navigating to ‘e-Pay Tax’ Section
- Visit the Income Tax Portal
- On the homepage, locate the ‘Quick Links’ section on the left side.
- Click on the ‘e-Pay Tax’ option or use the search bar to find ‘e-Pay Tax’.
Step 2: Enter PAN/TAN and Mobile Number
- Enter your PAN and re-enter to confirm it.
- Provide your mobile number and click ‘Continue
Step 3: Select the correct Assessment Year and Payment Type
- Select the first box labelled as ‘Income Tax’ and click ‘Proceed’
Step 4
1. From the ‘Assessment Year’ dropdown, select ‘2024-25’ for FY 23-24
- Under the ‘Type of Payment’, select ‘Self-Assessment Tax (300)’ and click on ‘Continue’. Enter the payment amounts accurately under the relevant categories.
Step 6: Verify Payment Information
- After clicking ‘Continue’, you can preview the challan details.
- Double-check the payment information for accuracy.
- Click ‘Pay Now’ to make the payment or ‘Edit’ to modify the details.
Step 7: Submit the Payment
- Tick the checkbox to agree to the Terms and Conditions.
- Click ‘Submit To Bank’ to proceed with the payment.
Step 8: Receive Payment Confirmation
- You will receive a confirmation once your tax payment has been successfully submitted.
Note: Remember to download the challan as you will need the BSR code and Challan number to complete the return filing process.